- Executive Resilience Insider
- Posts
- Why 70% of change efforts fail
Why 70% of change efforts fail
5 frameworks that build change reflexes
Organizations invest $250 billion annually in transformation technology and services while Gartner research reveals a brutal paradox: only 32% of change initiatives succeed in maintaining employee engagement and performance, while 79% of employees have lost trust in their organization's ability to change effectively. Cross-sector analysis demonstrates methodical miscalculation:
Corporate spending on change programs while 70% of initiatives fail to meet objectives
Leadership teams perfecting inspirational vision while employee willingness to support change collapsed from 74% in 2016 to 43% in 2022
Executives hiring transformation consultants while failed initiatives cost organizations 12% of annual revenue through wasted investment and opportunity deterioration
The Change Management Paradox:
Traditional investment ↑ = Employee trust ↓
More frequent change initiatives = Lower organizational capability
Rising transformation budgets destroy adaptive capacity
Reflexive change competence generates competitive multipliers faster than inspiration-driven campaigns create sustainable results.
Executives have 90 days to build comprehensive change intelligence or surrender advantages to competitors who understand that accumulated adaptability determines competitive survival.
Why inspiration-driven change management destroys organizational readiness
The average employee now experiences 10 planned enterprise changes annually. Up from 2 in 2016.
Organizations respond with elaborate transformation visions. Inspirational all-hands meetings. Consultants promising breakthrough results. Yet Gartner surveys reveal these approaches destroy the very capacity organizations need most.
Failed transformations waste $2.3 trillion globally. The conventional wisdom assumes employees need inspiration to embrace change. They need something else entirely: practiced reflexes that enable navigation through continuous uncertainty.
Consider Sarah Chen, VP of Operations at a $4 billion pharmaceutical company. Three years of perpetual reorganization had created what she called "initiative fatigue syndrome." Each new change initiative stalled within months. Employee surveys revealed something unexpected.
The problem wasn't resistance to change itself. Employees wanted their expertise to remain valuable. When the company introduced process automation, engineers pushed back because they feared their hard-won knowledge would become obsolete. Sarah's team developed a tool built around David Rock's SCARF model to help leaders understand the neurological threat responses driving resistance.
"We discovered that an employee's pushback on automation isn't really about whether the new process works," Sarah explains. "They're worried that their expertise will no longer be valuable. Once we uncovered this, we could provide reassurance: 'We will still count on your expertise to help us improve the new process.'"
The new process might still feel uncomfortable. But when employees understand why they feel uncomfortable, they move forward despite discomfort.
This represents the gap between inspiration approaches and reflex development:
Phase 1: Inspirational vision campaigns producing temporary enthusiasm followed by initiative fatigue
Phase 2: Structured skill-building through everyday practice enabling sustained adaptation
Phase 3: Change readiness as organizational muscle memory creating competitive edge
What separates winners from losers isn't superior inspiration. It's structured skill development.
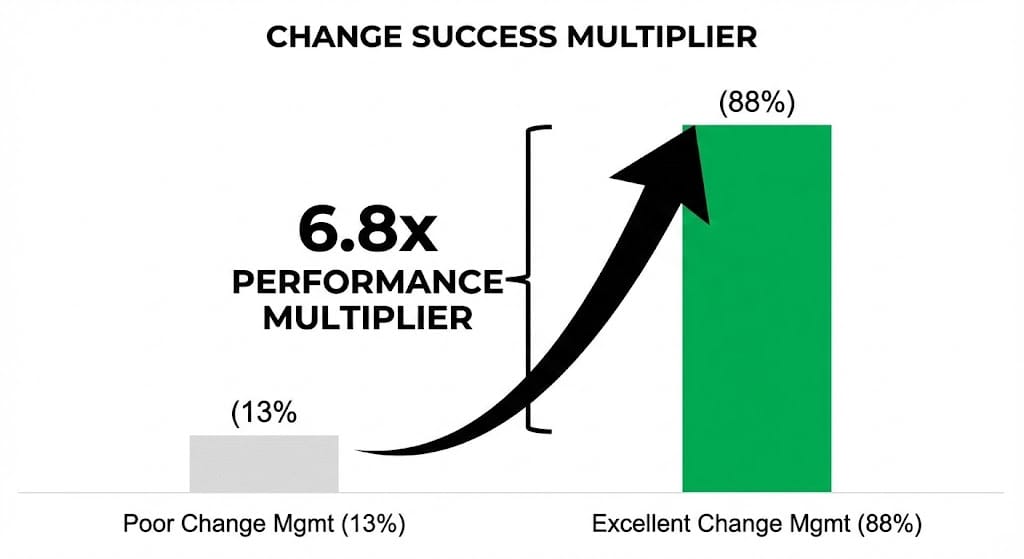
Organizations with excellent change management achieve 88% success in meeting objectives. Organizations with poor change management achieve 13% success. This 6.8x performance multiplier comes from practiced competence, not from better motivational speeches.
The change readiness methodology that competitive leaders discovered
Market leaders achieving breakthrough adaptation operate through fundamentally different philosophies. They've separated skill-building from inspiration requirements. The result: comprehensive reflex frameworks revealing positioning opportunities unavailable through traditional approaches.
The ungovernable change environment creates four convergence factors that inspiration cannot address. Changes stack simultaneously. Transformations continue without clear endpoints. Initiatives create complexity cascades through interdependencies. External disruptions demand rapid response capability.
Traditional change management treats each transformation as discrete event requiring fresh inspiration. What wins? Recognizing continuous change as operational reality requiring muscle memory rather than motivation.
The Change Readiness Formula:
Practiced reflexes + Everyday repetition + Psychological safety = Sustained adaptive edge
5 frameworks that transform change theater into readiness engines
Framework 1: The Journey Communication Protocol
Stop promising destinations. Start teaching navigation.
Traditional change messaging promotes transformation benefits, creating expectations that ungovernable change undermines. Journey protocols acknowledge uncertainty while clarifying that directional progress through small wins demonstrates skill development.
Continuous Journey Implementation
One U.S. bank restructured change communications around navigation rather than outcomes. Instead of announcing "We're becoming customer-centric by Q4," leaders frame transformations as ongoing journeys where consistent progress represents success.
They abandoned benefit promotion entirely. Too many broken promises had destroyed credibility. Instead, they created urgency by highlighting risks of inaction while reinforcing value through visible small wins.
Their communication framework uses four questions ensuring employees understand change context:
Why is the change occurring? Who is impacted by the change? What is the link to other changes? How could this change impact employees?
"Instead of promoting the benefits of changing, they create urgency by highlighting the risks of inaction. They reinforce the value of making progress by clarifying that consistent small wins on the change journey are the metric of success."
This eliminates destination dependency while building competitive edge through navigation understanding.
Strategic Transparency Design
Leaders pace communications deliberately. When teams aren't directly impacted, they share stories about changes occurring elsewhere, demonstrating organizational transformation reality without creating information overload.
The bank's approach differs fundamentally from traditional all-hands meetings promising breakthrough results. Employees hear: "Here's what's changing in product development. You're not affected yet, but you'll see how it connects to your work in Q2."
Transparency without noise. Context without overwhelm.
Framework 2: The Comfort-in-Discomfort Engine
Traditional change management builds enthusiasm. What actually works? Building psychological infrastructure that enables navigation through inherent uncertainty.
Emotional Regulation Strategy
Sarah Chen's pharmaceutical company discovered something counterintuitive. Change paralysis didn't stem from insufficient inspiration. Executives optimized for enthusiasm rather than building comfort with uncertainty.
The breakthrough came from reframing the problem. Rather than promising that benefits outweigh costs, effective leaders establish psychological safety through emotion regulation frameworks.
Her team's SCARF model application helped employees understand their negative responses. When you recognize that automation resistance often reflects expertise-value concerns rather than process effectiveness doubts, leaders can provide targeted reassurance. Employees move forward despite discomfort.
"We developed a tool for leaders to help them understand and respond to employee concerns. A leader could discover that an employee's pushback on process automation isn't about effectiveness. The employee worries their expertise will no longer be valuable."
Sarah's company saw something remarkable after implementing this approach. Engineers who'd resisted for months suddenly became implementation champions once they understood their concerns were addressed directly rather than dismissed through motivational messaging.
This psychological intelligence creates competitive edge through sustained navigation capacity. Traditional inspiration attempts generate temporary agreement through coordination processes lacking strategic credibility.
Psychological Safety Infrastructure
The data validates this approach. Organizations establishing psychological safety environments achieve 46% reduction in change fatigue.
How? By reframing experimentation failures as learning successes.
When employees feel supported taking calculated risks, organizations access critical frontline intelligence. This enables course correction when plans conflict with operational realities. Leaders hear honest feedback about what's actually working versus what sounds good in presentations.
Framework 3: The Change Reflex Accelerator
Traditional inspiration treats change as special event requiring extensive preparation. What wins? Integrating methodical skill-building through everyday practice that functions regardless of change velocity or complexity.
Six Core Reflexes Development
Gartner research identifies six reflexes applicable across transformation scenarios:
Being open to new experiences Effectively managing time Understanding business context Using technology effectively Working well with anyone regardless of prior experience Regulating emotions effectively
The key insight: these skills develop through what organizations call "micro-moments of change." Small situations occurring frequently enough for regular practice under lower-stress conditions.
A financial services firm implemented this deliberately. When leaders observe team members struggling with time management, they create natural coaching opportunities. "How would you adjust this timeline given these new priorities?" The question becomes practice rather than crisis intervention.
"Leaders identify coaching opportunities in micro-moments, tasks and activities that resemble employees' experiences during significant changes. These micro-moments occur frequently enough for regular practice under less stressful conditions."
These aren't formal training sessions. They're embedded in daily work. A project deadline shifts. A client changes requirements. Technology updates mid-sprint. Each becomes opportunity to practice adaptation reflexes.
Over time, these small repetitions compound into intuitive response patterns.
Practice Integration Protocol
Design skill development around operational reality rather than special events. The financial services firm discovered something counterintuitive: formal change management training had minimal impact. What worked? Managers coaching during normal work disruptions.
When software implementation reveals process redesign needs, employees with change reflexes independently adapt. They build new workflows as transformation evolves rather than waiting for guidance.
Framework 4: The Scenario Foresight Builder
Stop centralizing vision with leadership. Start distributing future-sensing across the organization.
Context-Sensing Implementation
A financial services firm discovered that waiting for leadership vision created strategic lag. By the time executives identified change requirements, market conditions had shifted again. Their solution? Empower teams to analyze likely future scenarios rather than waiting for direction.
Their context-sensing exercise works like this:
Leaders identify potential external triggers. Artificial intelligence advancement. Regulatory changes. Market disruptions.
Employees research assigned triggers and teach teams their findings.
Teams discuss likely future scenarios collaboratively.
Groups identify skills they'll need to respond effectively.
"Leaders identify potential external triggers that may cause organizational change. Employees research the trigger and teach the team what they learn. The team discusses likely future scenarios and skills they'll need to respond."
Over time, something remarkable happens. Employees develop intuitive understanding of emerging changes. They anticipate adaptation requirements before official announcements. Response capability accelerates dramatically.
The financial services firm reduced their change response time from months to weeks through this distributed intelligence approach. Sarah Chen's pharmaceutical company implemented similar context-sensing for regulatory changes, enabling her engineering teams to anticipate compliance requirements months before official announcements rather than scrambling reactively.
Distributed Intelligence Protocol
Traditional approaches centralize vision with leadership, requiring consensus validation on each scenario before developing response readiness. This creates strategic delays that competitors exploit.
Distributed foresight creates positioning edge through diverse perspective integration. When context-sensing becomes organizational reflex rather than leadership responsibility, companies identify adaptation requirements earlier and respond faster than inspiration-dependent competitors.
Framework 5: The Micro-Moment Practice Multiplier
Discrete transformation events don't build readiness. Continuous skill-building through everyday work compounds over time into sustainable competitive edge.
Everyday Practice Integration
Most organizations treat change management as episodic training. They schedule workshops. Hire consultants. Launch programs with fanfare. Then wonder why nothing sticks.
The micro-moment methodology recognizes that readiness develops through consistent practice rather than event-based training. It identifies routine activities resembling significant change experiences, creating natural opportunities for reflex-building.
Here's what this looks like in practice:
Software implementation reveals process redesign needs. Employees with change reflexes independently adapt and build new workflows as transformation evolves.
Client requirements shift mid-project. Teams with practiced reflexes adjust without escalation.
"When change changes, as is inevitable during ungovernable change, employees will have intuitive understanding of what to do next. Rather than waiting for guidance, employees with change reflexes can independently adapt."
The contrast is stark. Inspiration-dependent organizations require coordination processes that slow response velocity. Reflex-enabled teams act immediately because they've practiced similar disruptions dozens of times.
Cumulative Readiness Development
Microsoft's results validate this approach. After adopting reflex-based change methodology, they saw 450% increase in adoption rates. Half their customers reduced deployment times. Over 25,000 employees received training that focused on everyday practice rather than inspirational messaging.
Small repetitions compound. Daily practice accumulates. Over months and years, organizations with micro-moment focus develop muscle memory that inspiration-dependent competitors cannot replicate.
Building adaptive capacity transforms organizational paralysis
Developing change reflexes requires equivalent resources as inspiration approaches. The difference lies in allocation: toward methodical skill-building rather than motivation campaigns.
The performance gap is measurable. Organizations implementing deliberate reflex frameworks consistently outperform inspiration-dependent competitors. When motivation-focused companies experience strategic limitations during competitive pressure periods requiring rapid adaptation, reflex-enabled organizations respond automatically through practiced muscle memory.
The transformation window narrows daily.
Market leaders discover reflex-enabled advantages while establishing competitive positioning that inspiration excellence cannot replicate through communication mastery alone. They're building organizational muscle memory while competitors perfect their next all-hands presentation.
Companies implementing these frameworks within the next 90 days establish competitive advantages that inspiration-dependent executives cannot replicate through motivation refinement alone.